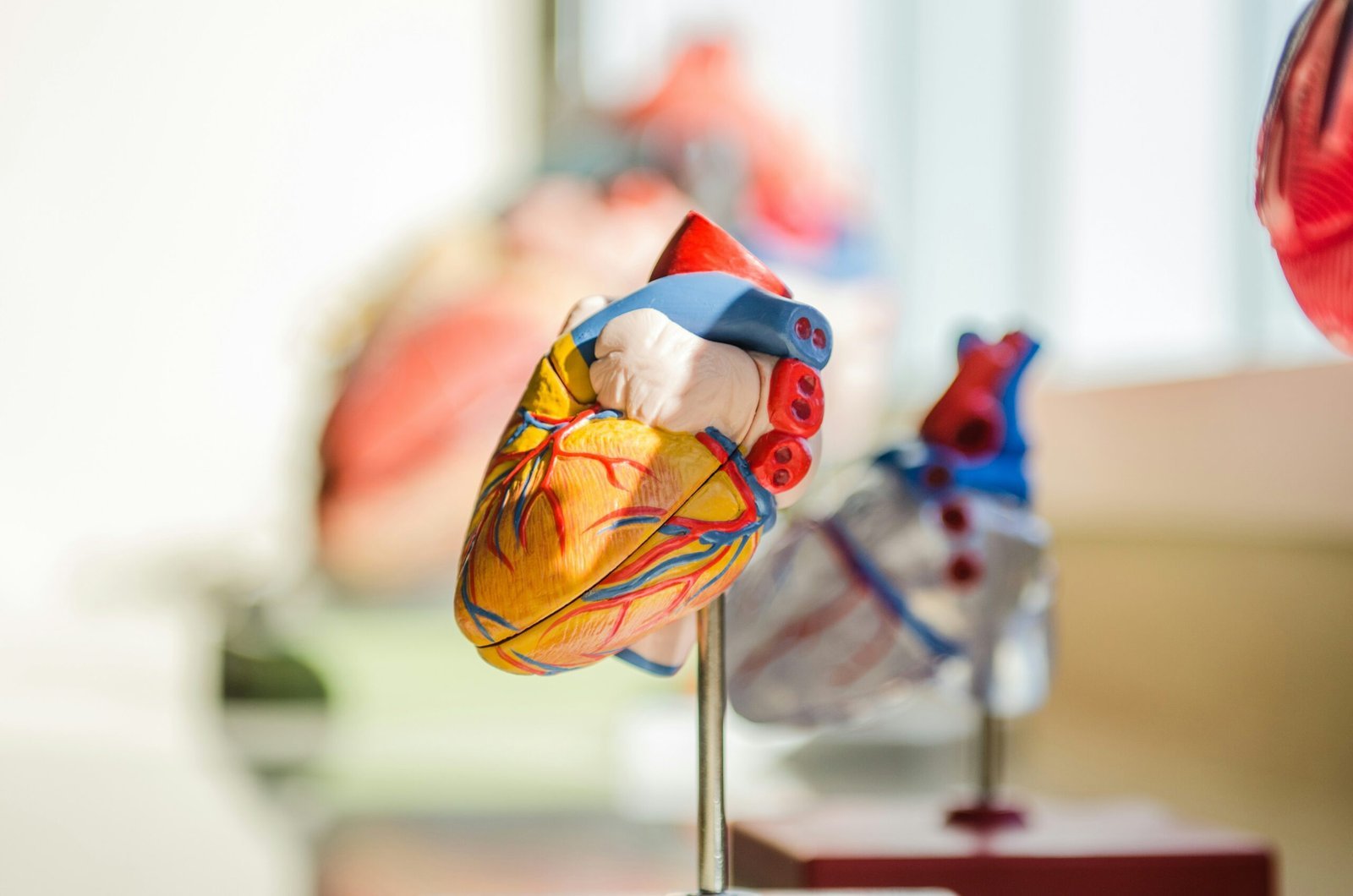
Understanding Heart Disease in Men
Heart disease remains one of the leading health concerns for men globally, accounting for a significant number of deaths annually. According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality worldwide, with men being disproportionately affected. In particular, men tend to develop heart disease at an earlier age compared to women, with studies indicating that men are more likely to experience heart attacks earlier in life, often due to a combination of biological and lifestyle factors.
Several key risk factors contribute to the prevalence of heart disease in men. These include high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Men are often more prone to engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, which can exacerbate these risk factors. Additionally, men generally have higher levels of stress and tend to ignore the early signs of heart disease, resulting in late diagnosis and treatment.
Biologically, men may be more predisposed to heart disease due to the influence of hormones, particularly testosterone, which may impact factors such as cholesterol levels and fat distribution. Furthermore, men typically have a higher incidence of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that occurs together, significantly raising the risk of heart disease. Awareness of these disparities is crucial, as early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
In light of these statistics and risk factors, it is vital for men to prioritize heart health through regular check-ups, lifestyle modifications, and education about the symptoms and warning signs of heart disease. By understanding the unique challenges that men face regarding heart health, they can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and enhance their overall well-being.
Identifying Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors associated with heart disease is crucial for men’s health. Some of the most significant contributors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes, smoking, and physical inactivity. Each of these factors plays a vital role in developing cardiovascular conditions, making awareness and assessment essential.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to damage over time. Men are often encouraged to monitor their blood pressure regularly, especially if they have a family history of heart disease. A reading above 130/80 mmHg may indicate hypertension, necessitating lifestyle changes or medical intervention.
High cholesterol is another key risk factor. The body produces two types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often dubbed “bad” cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), or “good” cholesterol. Elevated levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, restricting blood flow. Men should aim for total cholesterol levels below 200 mg/dL and regularly check their lipid profiles through blood tests.
Obesity is closely linked to heart disease due to the extra work required by the heart to pump blood through an increased body mass. Men can assess their weight-related risk by calculating their body mass index (BMI), with a BMI above 30 signaling obesity. This condition often coexists with diabetes, a metabolic disorder that affects how the body uses glucose and increases the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Additionally, smoking remains a leading preventable cause of heart disease. The harmful chemicals in tobacco damage blood vessels, promote plaque buildup, and reduce oxygen in the blood. Men who smoke should seek resources to quit, while those who don’t should avoid secondhand smoke exposure.
Lastly, physical inactivity can lead to weight gain and increased blood pressure. Men are encouraged to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week to help control their weight and improve cardiovascular health.
By identifying these risk factors, men can take proactive steps towards reducing their chances of developing heart disease, improving their overall wellbeing in the process.
Dietary Recommendations for Heart Health
Maintaining a heart-healthy diet is essential for reducing the risk of heart disease. One of the primary focuses should be on incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods that promote cardiovascular health. Fruits and vegetables are foundational components of this diet. Aim to fill half of your plate with colorful fruits and vegetables, as they are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help lower blood pressure and reduce cholesterol levels.
Whole grains also play a crucial role in heart health. Opt for whole-grain options such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread instead of refined grains. These foods are high in fiber, which aids in lowering cholesterol and improving heart function. In addition to fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, including healthy fats is essential for a balanced diet. Sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, which can help reduce bad cholesterol levels.
Conversely, certain foods should be limited or avoided to protect heart health. These include trans fats found in processed foods, excessive salt, and added sugars. Reducing intake of red and processed meats is also advisable, as they are often high in saturated fats. When planning meals, consider using herbs and spices to flavor food instead of salt and experimenting with plant-based proteins such as legumes and tofu, which can offer heart-healthy alternatives to meat.
Meal planning can significantly aid in maintaining a heart-healthy diet. Prepare a weekly menu, focusing on including a variety of the recommended food groups. Batch cooking grains and legumes can save time and ensure that you have nutritious options readily available. By making conscious dietary choices and being mindful of portion sizes, men can take active steps towards improving their heart health.
The Role of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of maintaining optimal heart health, particularly for men who may face increased risks of heart disease due to lifestyle factors. Engaging in consistent exercise not only supports cardiovascular health but also facilitates weight management, enhances cholesterol levels, and lowers blood pressure—all critical elements in heart disease prevention.
Authorities recommend that adults, including men, should strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Alternatively, 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activities like running or aerobic dancing may be considered. Additionally, it is advisable to include strength training exercises at least twice a week. This combination not only aids in weight reduction but also elevates metabolic rates, which are vital for overall well-being.
Aerobic exercises play a crucial role in heart health by improving blood circulation and enhancing the heart’s efficiency. These activities contribute to lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often termed ‘bad’ cholesterol, while simultaneously boosting high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as the ‘good’ cholesterol. Such changes in cholesterol profiles significantly reduce the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries, thereby lowering the chances of heart attacks and strokes.
Moreover, weight loss achieved through physical activity can directly influence blood pressure levels. Regular exercise helps regulate blood pressure by reducing blood vessel stiffness, enabling more efficient blood flow. Men should consider incorporating a mix of aerobic and strength training exercises into their routines to maximize heart health benefits. As with any health initiative, it is recommended that individuals consult healthcare professionals to develop personalized fitness plans suitable for their health status and goals.
Managing Stress for Heart Health
Stress significantly influences heart health, particularly in men. Chronic stress can lead to dangerous cardiovascular conditions, as it increases blood pressure, promotes unhealthy behaviors, and triggers the release of harmful hormones. The connection between stress and heart disease is increasingly recognized, making it vital for men to develop effective strategies for managing stress.
One of the most beneficial methods for stress management is mindfulness. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and promote greater emotional regulation. Regularly setting aside time to engage in mindfulness not only allows individuals to address their stress levels but also encourages a healthier perspective on life’s challenges, potentially mitigating their impacts on heart health.
Exercise is another powerful tool against stress, contributing to both mental well-being and cardiovascular health. Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Activities such as walking, jogging, or participating in team sports can be tailored to individual preferences, making it easier to incorporate them into a weekly routine. Men should aim to include at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, as recommended by health professionals.
Relaxation techniques, such as yoga or tai chi, also promote stress reduction while enhancing flexibility and overall physical health. These practices combine physical movement with focused breathing and meditation, allowing participants to unwind and rebalance their bodies and minds. Setting aside time for relaxation can greatly improve daily focus and emotional resilience.
Ultimately, integrating these effective stress management techniques into daily routines can reduce stress and protect heart health. By prioritizing stress management, men can take proactive steps toward maintaining cardiovascular wellness and enhancing their overall quality of life.
Regular Health Screenings
Regular health screenings are a fundamental aspect of maintaining heart health, particularly for men who may be at a higher risk for heart disease. Early detection of potential risk factors, such as elevated blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes, can significantly influence outcomes and improve overall health. These screenings serve as a proactive measure, allowing men to address health issues before they escalate into more serious conditions.
Blood pressure checks are vital, as hypertension often presents no symptoms but can lead to serious complications if left unchecked. It is recommended that men begin regular blood pressure screenings at age 40, or earlier if they have a family history of heart disease or other risk factors. Maintaining blood pressure within a healthy range is crucial to reducing the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
Cholesterol testing is equally important, as it helps determine levels of both LDL (bad cholesterol) and HDL (good cholesterol). Men should undergo cholesterol tests starting at age 35, or at 20 if they possess risk factors such as obesity or smoking. The American Heart Association recommends that men aim for an LDL level below 100 mg/dL to mitigate cardiovascular risks.
Diabetes screenings are essential as diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart disease. Men aged 45 and older should be screened for diabetes, particularly if they are overweight or have additional risk factors. Those with prediabetes should also have regular follow-ups to monitor their condition closely.
Men should make it a priority to consult their healthcare providers regarding a personalized screening schedule that factors in age, family history, and lifestyle. By prioritizing these essential screenings, men can effectively manage their heart health and take necessary strides toward reducing the risk of heart disease.
Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol
Tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption are significant contributors to heart disease, one of the leading causes of mortality among men worldwide. Smoking is particularly detrimental to cardiovascular health; studies indicate that smokers are twice as likely to develop heart disease compared to non-smokers. In fact, the American Heart Association reports that smoking is responsible for approximately 30% of all coronary heart disease deaths. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke damage blood vessels, promote plaque buildup and reduce the oxygen that reaches the heart, leading to an increased risk of heart complications.
Quitting smoking can significantly improve heart health. There are numerous strategies that can assist individuals in their transition away from tobacco. One effective approach is utilizing nicotine replacement therapies, which may include patches, chewing gum, or lozenges. Behavioral therapies, such as counseling or support groups, can also provide essential assistance. Furthermore, setting a quit date, removing triggers associated with smoking, and seeking support from friends and family can increase chances for success. The journey may be challenging, but the long-term benefits for heart health are considerable.
When it comes to alcohol, moderation is key. While some studies suggest that moderate alcohol consumption might offer certain cardiovascular benefits, excessive drinking significantly raises the risk of heart disease. For men, the recommended limit is up to two drinks per day. It is crucial to define what constitutes a standard drink: approximately 14 grams of pure alcohol, which equates to about 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits. By adhering to these guidelines and practicing moderation, men can help protect their heart health while enjoying social occasions.
The Importance of Sleep
Sleep is a fundamental aspect of overall health, and its significance cannot be overstated when it comes to heart health, especially for men. Inadequate sleep has been linked to various adverse cardiovascular effects, including hypertension (high blood pressure), which is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Research has shown that men who regularly sleep less than the recommended amount are more likely to develop hypertension, obesity, and other related health issues, creating a concerning cycle that can endanger heart health.
The recommended amount of sleep for adults is generally between 7 to 9 hours per night. Achieving this optimal duration can foster improved cardiovascular function and lower the risk of heart disease. Consistent sleep patterns play a critical role as well; maintaining a regular sleep schedule helps regulate the body’s internal clock, which can enhance sleep quality and the overall restorative process that occurs during slumber. Establishing a fixed bedtime and wake-up time can contribute notably to better long-term health outcomes.
To improve sleep hygiene, individuals can adopt several strategies. Creating a comfortable sleep environment is essential; this includes a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom. Limiting screen time before bed helps the body to wind down by reducing blue light exposure, which can interfere with the natural production of melatonin. Additionally, engaging in relaxation techniques such as reading, meditating, or taking a warm bath can effectively signal the body that it is time to sleep.
Moreover, regular physical activity has been linked to better sleep quality, but it is advisable to schedule workouts earlier in the day rather than close to bedtime. Avoiding large meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bed can also significantly impact the ability to fall and stay asleep. By prioritizing sleep hygiene and recognizing its importance, men can take proactive steps towards maintaining heart health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular issues.
Building a Support System
Maintaining heart health is crucial for men, and one often overlooked aspect is the importance of a robust support system. Friends and family can play a pivotal role in encouraging healthy habits and providing accountability in lifestyle changes, which are essential in reducing the risk of heart disease. The emotional and psychological support from loved ones not only fosters motivation but also helps create a positive environment where healthier choices are more easily adopted.
Engaging with a community can also enhance one’s commitment to a heart-healthy lifestyle. Men are encouraged to connect with peers who share similar health goals, whether through exercise groups, cooking classes, or online forums that focus on heart health. This interaction can provide a sense of camaraderie, making it easier to stay motivated through shared experiences and challenges. Additionally, men should not hesitate to seek professional guidance from healthcare providers. Regular check-ins with medical professionals can offer crucial insights into personal health metrics and reinforce the importance of adhering to prescribed lifestyle recommendations.
Furthermore, men should actively communicate their health goals with their close network. This openness not only facilitates understanding but also invites support in various forms, such as joining in on physical activities or offering healthier meal options. Establishing routines where friends come together for activities—like walking, running, or playing sports—can make the process enjoyable and sustainable. Overall, a support system rich in engagement can significantly ease the journey toward improved heart health by making lifestyle modifications feel more attainable and less isolating.